Agile Prototyping






Agile prototyping in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is an iterative, flexible approach that leverages CNC technology to rapidly create, test, and refine physical prototypes. This approach allows designers, engineers, and manufacturers to efficiently bring new product ideas to life by producing tangible models that can be evaluated and adjusted based on feedback from each iteration.
Here’s a breakdown of what to do with agile prototyping
Define Requirements: Start by establishing the design objectives, material needs, and functionality requirements for the part or product. This will guide the initial prototype.
Create a Digital Model: Develop a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model that serves as the blueprint for the prototype. This digital model can be easily modified as needed throughout the prototyping process.
Set Up CNC Machining: Translate the CAD model into a CNC-compatible format, and set up the CNC machine with the right tooling, materials, and settings to achieve the desired precision.
Produce the First Prototype: Machine the first iteration of the prototype, paying attention to the specific tolerances and finishes required. CNC’s accuracy and repeatability ensure high-quality results with each iteration.
Evaluate and Gather Feedback: Assess the prototype for functionality, fit, and finish. Gather feedback from stakeholders, designers, or potential users to identify any necessary changes.
Refine the Design: Modify the CAD model based on feedback and make any needed adjustments to the CNC setup. With agile prototyping, these changes are easy to implement in the digital model and the machining process.
Repeat as Necessary: Continue the cycle of producing, evaluating, and refining the prototype until it meets the design and functionality requirements.
Finalize the Product: Once the prototype is perfected, the final design can transition smoothly into full production, leveraging the CNC settings and specifications developed during prototyping.
By integrating agile methods with CNC machining, teams can quickly adapt to changes, reduce production time, and improve the quality of the final product while minimizing waste. This iterative process makes CNC-based agile prototyping ideal for custom parts manufacturing, enabling efficient development and faster market entry.
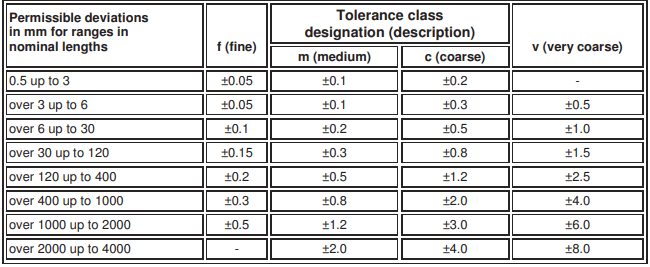
General Tolerance